# librerias requeridas
library(sf)
library(mapview)
library(dplyr)SIG con R: Vectores part 2
SIG
R
Apuntes de la escuela ambiental
Continuación de apuntes con manipulación y operación con vectores
Crear polígonos mínimos convexos
En ecología y biología nos ayuda para determinar hábitos hogareños, es decir, encontrar el área en el que se desplaza una especie.
# Cargamos el dataframe con los puntos
registros<-read.csv("Registros.csv", header = T) %>% st_as_sf(coords=c("Longitude","Latitude"), crs=4326)
mapview(registros)# Observar solo la sp1
sp1<-filter(registros, Species=="sp1")
mapview(sp1)# Generar PMC para una sola especie
pmc1<- sp1 %>% group_by(Species) %>%
summarise(geometry= st_combine(geometry)) |> st_convex_hull()
mapview(list(pmc1, sp1))# Generar poligonos para todas las especies
pmc_spp<- registros %>% group_by(Species) %>%
summarise(geometry= st_combine(geometry)) %>%
st_convex_hull()
mapview(list(pmc_spp, registros))Crear polígonos alpha hull
#install.packages("alphahull")
#instalar maptools
#("maptools", repos = "https://packagemanager.posit.co/cran/2023-10-13")
library(maptools)
library(alphahull)
library(sp)
#library(rgdal)# Funcion para convertir los a-hull en shp (https://stat.ethz.ch/pipermail/r-sig-geo/2012-March/014409.html)
ah2sp <- function(x, increment=360, rnd=10, proj4string=CRS(as.character(NA))){
require(alphahull)
require(maptools)
if (class(x) != "ahull"){
stop("x needs to be an ahull class object")
}
# Extract the edges from the ahull object as a dataframe
xdf <- as.data.frame(x$arcs)
# Remove all cases where the coordinates are all the same
xdf <- subset(xdf,xdf$r > 0)
res <- NULL
if (nrow(xdf) > 0){
# Convert each arc to a line segment
linesj <- list()
prevx<-NULL
prevy<-NULL
j<-1
for(i in 1:nrow(xdf)){
rowi <- xdf[i,]
v <- c(rowi$v.x, rowi$v.y)
theta <- rowi$theta
r <- rowi$r
cc <- c(rowi$c1, rowi$c2)
# Arcs need to be redefined as strings of points. Work out the number of points to allocate in this arc segment.
ipoints <- 2 + round(increment * (rowi$theta / 2),0)
# Calculate coordinates from arc() description for ipoints along the arc.
angles <- anglesArc(v, theta)
seqang <- seq(angles[1], angles[2], length = ipoints)
x <- round(cc[1] + r * cos(seqang),rnd)
y <- round(cc[2] + r * sin(seqang),rnd)
# Check for line segments that should be joined up and combine their coordinates
if (is.null(prevx)){
prevx<-x
prevy<-y
} else if (x[1] == round(prevx[length(prevx)],rnd) && y[1] ==
round(prevy[length(prevy)],rnd)){
if (i == nrow(xdf)){
#We have got to the end of the dataset
prevx<-append(prevx,x[2:ipoints])
prevy<-append(prevy,y[2:ipoints])
prevx[length(prevx)]<-prevx[1]
prevy[length(prevy)]<-prevy[1]
coordsj<-cbind(prevx,prevy)
colnames(coordsj)<-NULL
# Build as Line and then Lines class
linej <- Line(coordsj)
linesj[[j]] <- Lines(linej, ID = as.character(j))
} else {
prevx<-append(prevx,x[2:ipoints])
prevy<-append(prevy,y[2:ipoints])
}
} else {
# We have got to the end of a set of lines, and there are several such sets, so convert the whole of this one to a line segment and reset.
prevx[length(prevx)]<-prevx[1]
prevy[length(prevy)]<-prevy[1]
coordsj<-cbind(prevx,prevy)
colnames(coordsj)<-NULL
# Build as Line and then Lines class
linej <- Line(coordsj)
linesj[[j]] <- Lines(linej, ID = as.character(j))
j<-j+1
prevx<-NULL
prevy<-NULL
}
}
# Promote to SpatialLines
lspl <- SpatialLines(linesj)
# Convert lines to polygons
# Pull out Lines slot and check which lines have start and end points that are the same
lns <- slot(lspl, "lines")
polys <- sapply(lns, function(x) {
crds <- slot(slot(x, "Lines")[[1]], "coords")
identical(crds[1, ], crds[nrow(crds), ])
})
# Select those that do and convert to SpatialPolygons
polyssl <- lspl[polys]
list_of_Lines <- slot(polyssl, "lines")
sppolys <- SpatialPolygons(list(Polygons(lapply(list_of_Lines, function(x)
{ Polygon(slot(slot(x, "Lines")[[1]], "coords")) }), ID = "1")),
proj4string=proj4string)
# Create a set of ids in a dataframe, then promote to SpatialPolygonsDataFrame
hid <- sapply(slot(sppolys, "polygons"), function(x) slot(x, "ID"))
areas <- sapply(slot(sppolys, "polygons"), function(x) slot(x, "area"))
df <- data.frame(hid,areas)
names(df) <- c("HID","Area")
rownames(df) <- df$HID
res <- SpatialPolygonsDataFrame(sppolys, data=df)
res <- res[which(res@data$Area > 0),]
}
return(res)
}puntos<- read.csv("Registros.csv", header=TRUE)
sp1<-puntos %>% filter(Species=="sp1")Defino Alfa y creo el poligono (el valor de alfa debe variar segun los puntos). En los datos NO deben haber x, y duplicados, sino la funcion saca ERROR. Los datos ya deben estar limpios
# Alfa hull
alpha=4.5 # ancho de poligono
1alfa_sp1<-ahull(x=sp1$Longitude, y=sp1$Latitude, alpha=alpha)
plot(alfa_sp1)- 1
- Comando del paquete alphahull
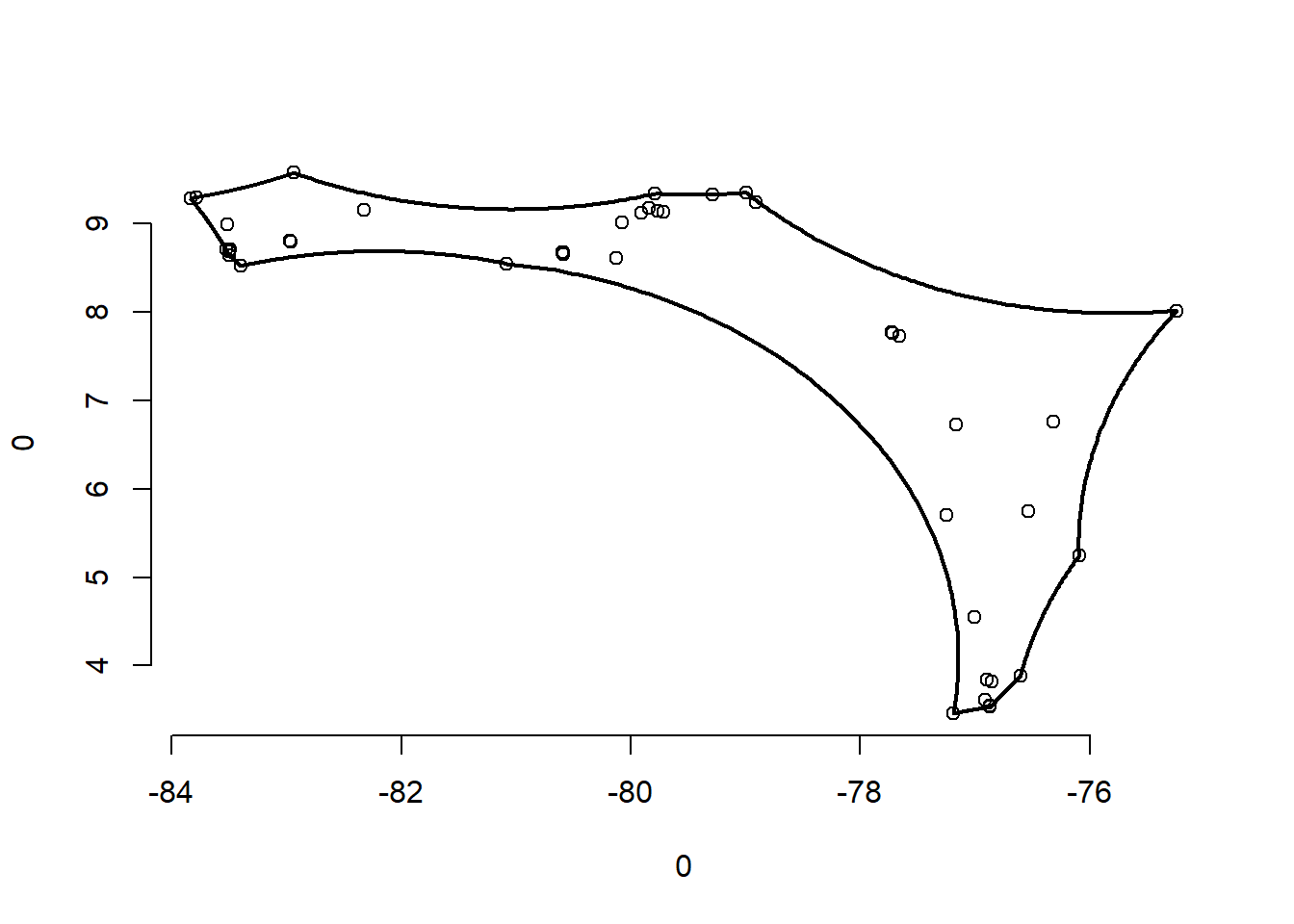
class(alfa_sp1)[1] "ahull"# transformo de ashape a spatial polygon
ob_shape<-ah2sp(alfa_sp1)
plot(ob_shape)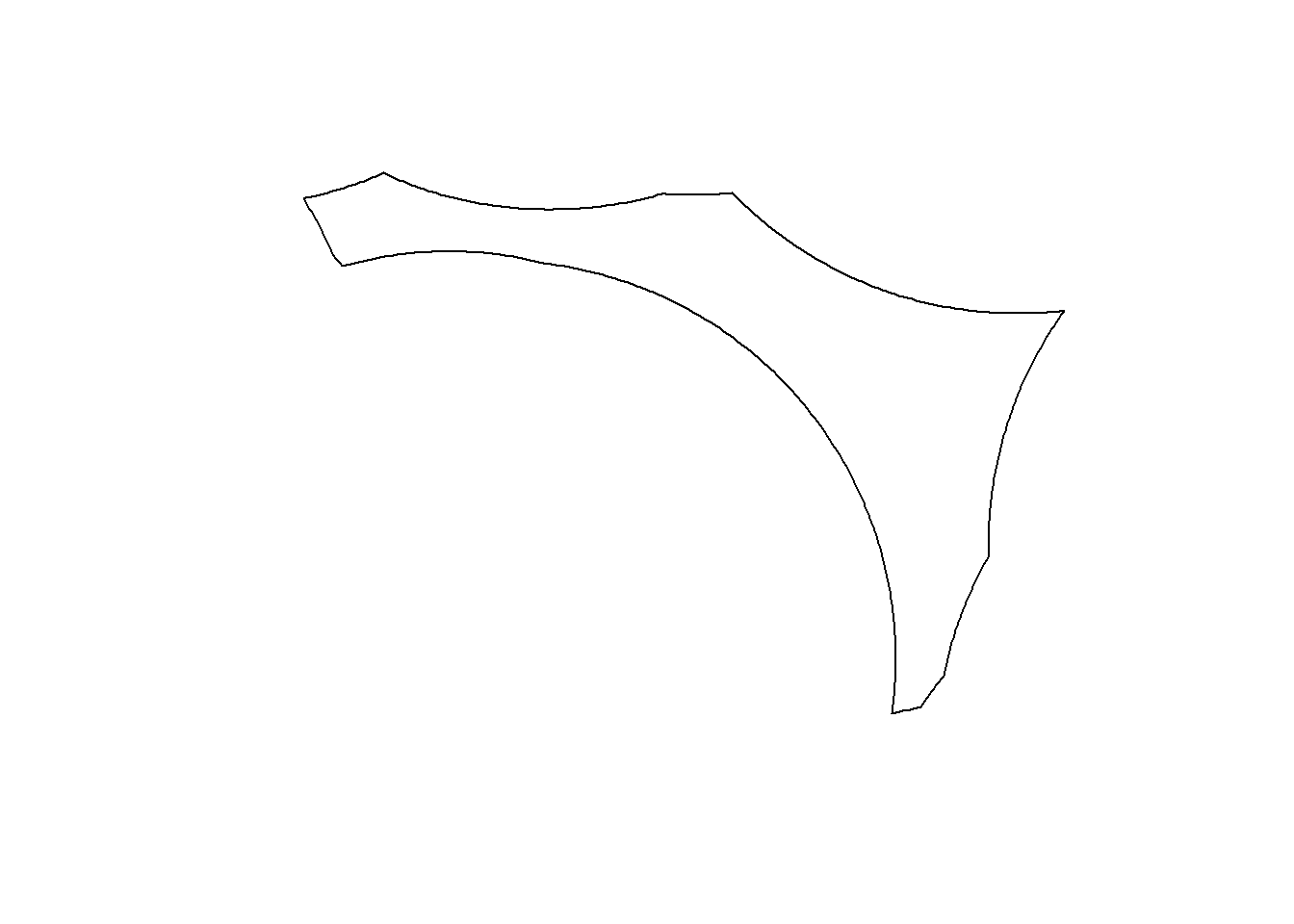
class(ob_shape)[1] "SpatialPolygonsDataFrame"
attr(,"package")
[1] "sp"# Exporto shape. Debo configurar el dsn.
# write_sf(obs_shp, "alpha_hull.shp")Búferes
¿ Cómo dibujar un área sobre sobre un polígono ?
# librerias requeridas
library(sf)
library(mapedit)
library(mapview)
library(tidyverse)# para dibujar los shapefile
poligono <-mapview() %>% editMap()
puntos <-mapview() %>% editMap()
lineas <-mapview() %>% editMap()
mapview(poligono$drawn)
#transformar sistemas de coordenadas
polig<- poligono$finished %>% st_transform(crs=32618)
point<- puntos$finished %>% st_transform(crs=32618)
rutas<- lineas$finished %>% st_transform(crs=32618)
mapview(list(polig, point, rutas))# write_sf(poligono$drawn, "polig.shp")Tengan en cuenta que el sistema de coordenadas de referencia nos marca las unidades de distancia (En este caso el sistema de coordenadas esta en UTM y trabaja las distancias en metros). Si quieren que las unidades sean metros deben reproyectar su capa. 1 km equivale a aproximadamente 0.0083333 grados
# creando buffer
1polibuff<-st_buffer(polig, dist= 10000)
mapview(list(polig, polibuff))
puntbuff<-st_buffer(point, dist= 5000)
mapview(list(point, puntbuff))
linbuff<-st_buffer(rutas, dist= 500)
mapview(list(rutas, linbuff))- 1
- la distancia este en metros 😀 que equivalen a 10 km
# buffer negativo
polibuff2<-st_buffer(polig, dist= -10000)
mapview(list(polig, polibuff, polibuff2))Calculando áreas
# Calculo de areas
1a_po<-st_area(polig)/1000000
a_pb<-st_area(polibuff)/1000000
a_pb2<-st_area(polibuff2)/1000000- 1
- Se divide entre un millón para pasar de \(m^2\) a \(km^2\)
areakm2<-c(a_po, a_pb, a_pb2)
# calculando diferencias entre los poligonos
areakm2[1]-areakm2[2]
areakm2[1]-areakm2[3]col<- read_sf("COL_adm1.shp")
area_col<-st_area(col)/1000000
#calculo de areas de departamentos
areas_depa<- col %>% mutate(AREAKM=st_area(col)/1000000)